
The oxygen has two lone pairs, one of which occupies a p orbital perpendicular to the ring on that position, thereby maintaining the conjugation of that five-membered ring by overlap with the perpendicular p orbital on each of the adjacent carbon atoms. For example, furan is a five-membered ring with two alternating double bonds flanking an oxygen. As long as each contiguous atom in a chain has an available p orbital, the system can be considered conjugated. However, that is not the only way for conjugation to take place. (Particular attention should be paid to the involvement or non-involvement of "non-bonding" electrons.)Ĭonjugation is possible by means of alternating single and double bonds in which each atom supplies a p orbital perpendicular to the plane of the molecule. Atoms involved are in bold red, while electrons involved in delocalized bonding are in blue. Second row: allyl radical, acetate ion, acrolein. Top row: pyridine, furan, tropylium cation.

Some prototypical examples of species with delocalized bonding.
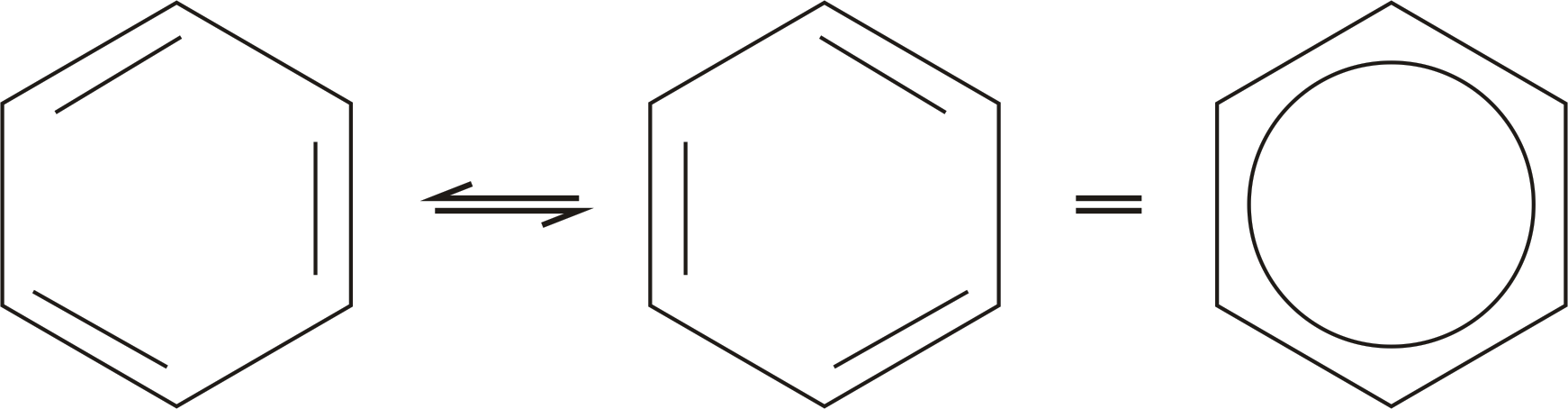
The largest conjugated systems are found in graphene, graphite, conductive polymers and carbon nanotubes.Ĭhemical bonding in conjugated systems Some simple organic conjugated molecules are 1,3-butadiene, benzene, and allylic carbocations. Molecules containing conjugated systems of orbitals and electrons are called conjugated molecules, which have overlapping p orbitals on three or more atoms. The π electrons do not belong to a single bond or atom, but rather to a group of atoms. They allow a delocalization of π electrons across all the adjacent aligned p-orbitals. Ī conjugated system has a region of overlapping p-orbitals, bridging the interjacent locations that simple diagrams illustrate as not having a π bond. Ĭonjugation is the overlap of one p-orbital with another across an adjacent σ bond (in transition metals, d-orbitals can be involved). The term "conjugated" was coined in 1899 by the German chemist Johannes Thiele.

Lone pairs, radicals or carbenium ions may be part of the system, which may be cyclic, acyclic, linear or mixed. It is conventionally represented as having alternating single and multiple bonds. In theoretical chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in a molecule, which in general lowers the overall energy of the molecule and increases stability.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
